by admin | Aug 31, 2023 | Renewable Energy Technologies, Technology
What are Renewable Energy Technologies?
Renewable energy technologies are technologies that harness energy from naturally replenishing sources that are practically inexhaustible over human timescales. These sources of energy are considered sustainable and environmentally friendly because they have a much lower impact on the environment compared to fossil fuels, which are finite and contribute to pollution and climate change.
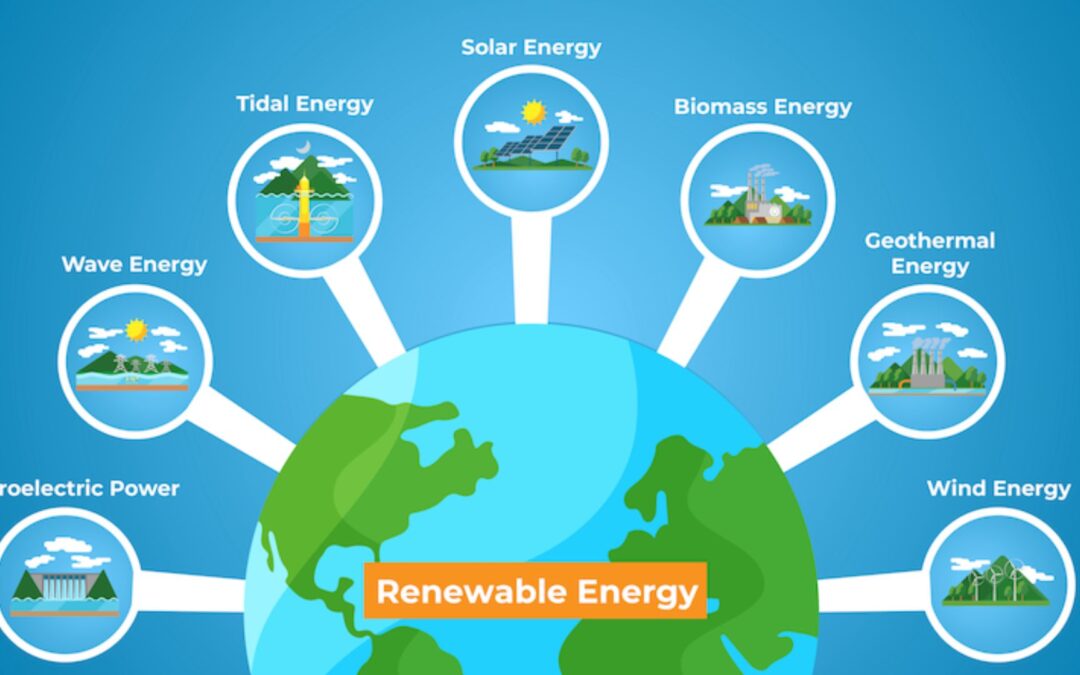
Here are some key types of renewable energy technologies:
- Solar Energy: Solar energy involves capturing sunlight and converting it into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) cells or heat-using solar thermal systems. Solar panels on rooftops and solar farms are common applications.
- Wind Energy: Wind energy is generated by wind turbines that convert the kinetic energy of wind into electricity. Wind farms with multiple turbines are installed in locations with consistent wind patterns.
- Hydroelectric Power: Hydroelectric power is generated by harnessing the energy of flowing water, usually from rivers or dams, and converting it into electricity using turbines and generators.
- Geothermal Energy: Geothermal energy utilizes heat from the Earth’s interior. Geothermal power plants capture this heat to produce electricity, and geothermal heating systems provide direct heat for residential and commercial use.
- Biomass Energy: Biomass energy comes from organic materials such as wood, agricultural residues, and organic waste. It can be used for heating, electricity generation, and even biofuels.
- Ocean Energy: Ocean energy includes tidal energy, generated by the rise and fall of tides, and wave energy, harnessed from the motion of ocean waves.
Renewable energy technologies offer several benefits:
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Renewable energy sources produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions, helping mitigate climate change.
- Energy Independence: Relying on renewable sources reduces dependence on imported fossil fuels, enhancing energy security.
- Job Creation: The renewable energy sector creates jobs in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and research.
- Sustainable Development: Renewable energy supports sustainable development by providing clean and reliable energy for communities.
- Lower Environmental Impact: Unlike fossil fuels, renewable sources have minimal air and water pollution impacts, reducing damage to ecosystems.
- Diversification of Energy Sources: A mix of renewable sources diversifies the energy portfolio, increasing resilience against energy supply disruptions.
However, renewable energy technologies also face challenges, including intermittency (e.g., solar energy is not generated at night), initial high costs (though they have been decreasing), and the need for suitable infrastructure and energy storage solutions.
As society’s awareness of climate change and environmental concerns grows, renewable energy technologies are increasingly being adopted as a crucial part of global efforts to transition to a more sustainable and low-carbon energy future.
by admin | Aug 31, 2023 | Technology, What is Natural Language Processing
What is Natural Language Processing?
Natural Language Processing( NLP) is a element of artificial intelligence( AI) that focuses on the relationship between computers and mortal language. The thing of NLP is to make computers to comprehend, interpret, produce, and respond to mortal language in a way that’s both meaningful and precious.
NLP involves a range of tasks that allow computers to work with human language, including:
- Text Understanding: This includes tasks like sentiment analysis (determining the emotional tone of a text), named entity recognition (identifying entities like names, dates, and locations), and text classification (categorizing text into predefined categories).
- Language Generation: NLP systems can generate human-like language, such as in chatbots, language translation, and content generation.
- Speech Recognition: NLP enables computers to convert spoken language into text, facilitating voice commands and transcription services.
- Language Translation: NLP systems can translate text from one language to another, making global communication more accessible.
- Question Answering: NLP systems can process and understand questions posed in natural language and provide relevant answers, as seen in virtual assistants.
- Text Summarization: NLP can automatically generate concise summaries of longer texts, aiding in information extraction and content understanding.
- Language Modeling: NLP models can learn patterns and structures in language, which is useful for various applications, including predictive typing and autocomplete suggestions.
- Topic Modeling: This involves identifying and extracting topics from large collections of text data.
- Dialog Systems: NLP powers chatbots and virtual assistants that can engage in natural language conversations with users.
NLP algorithms and models use various techniques, including machine learning, deep learning, and statistical methods. Some of the most prominent NLP models, like transformer models, have achieved remarkable results by understanding context and semantics in text data.
Challenges in NLP include handling ambiguity, understanding context, dealing with different languages and dialects, and capturing nuances of human communication. NLP has a wide range of applications across industries:
- Customer Support: NLP powers chatbots and virtual agents that can handle customer queries and support requests.
- Search Engines: NLP enhances search engines by understanding user queries and providing more relevant results.
- Social Media Analysis: NLP is used to analyze and understand social media sentiment, trends, and user behavior.
- Healthcare: NLP helps process medical records, extract insights from clinical notes, and assist in medical research.
- Language Translation: NLP systems like Google Translate enable rapid and accurate translation between languages.
- Content Generation: NLP can generate news articles, summaries, and other content automatically.
- Legal and Compliance: NLP aids in analyzing legal documents, contracts, and regulations for compliance and understanding.
NLP is a rapidly advancing field, and recent developments, including large pre-trained language models like GPT-3, have demonstrated significant progress in understanding and generating human-like language.
by admin | Aug 31, 2023 | Technology, What is Internet of Things
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical objects, devices, vehicles, buildings, and other items embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity capabilities that enable them to collect and exchange data over the Internet. Essentially, IoT extends the reach of the internet beyond traditional computing devices like computers and smartphones to include a wide variety of everyday objects and “things.”
The key characteristics and components of IoT include:
- Connectivity: IoT devices are equipped with various communication technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks, and more, enabling them to communicate with each other and with central systems.
- Sensors and Actuators: IoT devices are equipped with sensors to collect data from their environment (e.g., temperature, humidity, light) and actuators to perform actions based on that data (e.g., turning on a fan).
- Data Collection and Analysis: IoT devices gather and transmit data to centralized systems or cloud platforms where the data is analyzed to derive insights and make informed decisions.
- Automation and Control: IoT enables automation by allowing devices to interact with each other and make autonomous decisions based on predefined rules or machine learning algorithms.
- Remote Monitoring and Management: IoT devices can be remotely monitored and managed, making it possible to control devices and receive real-time updates from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Interoperability: IoT systems often involve a diverse range of devices from different manufacturers. Interoperability standards are crucial to ensure seamless communication and integration.
- Scalability: IoT networks can accommodate a vast number of devices, ranging from a few to millions, making them highly scalable.
Applications of IoT span across various industries:
- Smart Home: IoT devices in homes can control lighting, thermostats, security cameras, and appliances remotely for increased comfort, energy efficiency, and security.
- Healthcare: IoT enables remote patient monitoring, smart medical devices, and healthcare systems that improve patient outcomes and streamline healthcare delivery.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): In industrial settings, IoT is used for predictive maintenance, asset tracking, process optimization, and real-time monitoring of machinery and equipment.
- Smart Cities: IoT contributes to the development of smart cities through applications like smart traffic management, waste management, environmental monitoring, and energy efficiency.
- Agriculture: IoT sensors can monitor soil conditions, weather, and crop health, enabling precision agriculture and efficient resource utilization.
- Retail: IoT is used for inventory management, personalized customer experiences, and supply chain optimization.
- Transportation and Logistics: IoT enhances fleet management, real-time tracking of goods, and optimization of transportation routes.
- Energy Management: IoT helps manage and optimize energy consumption in buildings and grids, contributing to energy efficiency and sustainability.
While IoT offers numerous benefits, it also poses challenges related to data security, privacy, interoperability, and the sheer complexity of managing a vast number of devices. As IoT technology continues to advance, it has the potential to revolutionize industries and create innovative solutions to complex problems.
by admin | Aug 31, 2023 | Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality, Technology
What is Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are immersive technologies that alter our perception of the real world and create interactive digital experiences. While they share similarities, they serve different purposes and offer distinct user experiences.
Augmented Reality (AR):
Augmented Reality involves overlaying digital content, such as images, videos, and 3D models, onto the real-world environment. This is typically done through devices like smartphones, tablets, AR glasses, or even heads-up displays in vehicles. AR enhances our perception of reality by adding virtual elements that interact with and augment the physical world.
Key features of AR include:
- Real-time Interaction: AR enables users to interact with digital objects in real-time within their immediate environment.
- Integration with Reality: Virtual objects are integrated into the user’s actual surroundings, making it possible to blend the virtual and real worlds.
- Applications: AR has applications in various fields, from gaming and entertainment to education, healthcare, navigation, architecture, and marketing.
- Examples: Pokémon GO is a popular AR game that lets players catch virtual creatures in the real world. AR navigation apps overlay directions onto the live view from a smartphone’s camera.
Virtual Reality (VR):
Virtual Reality, on the other hand, creates an entirely simulated environment that users can interact with. VR typically requires specialized hardware, such as VR headsets, to fully immerse users in the virtual world. In VR, users are completely isolated from the physical environment and are surrounded by computer-generated content.
Key features of VR include:
- Immersive Environment: VR provides a fully immersive experience, transporting users to a virtual environment where they can interact with objects and surroundings.
- Isolation from Reality: Users wearing VR headsets are visually and often aurally cut off from the real world, allowing them to focus entirely on the virtual experience.
- Applications: VR finds applications in gaming, training simulations (e.g., flight simulators), virtual tourism, medical training, architectural visualization, and more.
- Examples: Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, and PlayStation VR are popular VR headset platforms used for gaming and other immersive experiences.
In summary, while both AR and VR offer immersive experiences, AR enhances the real world by overlaying digital content it, and VR creates a completely virtual environment that users can interact with. Both technologies have the potential to transform industries and create new ways for people to engage with digital content and information.

by admin | Aug 31, 2023 | Cybersecurity, Technology
what is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, data, and digital assets from various forms of cyber threats, attacks, and unauthorized access. It encompasses a wide range of technologies, processes, practices, and measures designed to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of digital information.
The primary goal of cybersecurity is to safeguard information and digital resources from:
- Cyberattacks: Deliberate and malicious attempts to breach or compromise computer systems, networks, or data. Examples include malware (viruses, worms, ransomware), phishing attacks, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive data, leading to its theft or exposure. This could involve personal information, financial data, intellectual property, and more.
- Hacking: Unauthorized intrusion into computer systems, often with the intent to manipulate or steal data, disrupt operations, or gain control.
- Identity Theft: Unauthorized acquisition and misuse of personal information, often for financial gain.
- Espionage: Cyber activities conducted by governments, organizations, or individuals to gather intelligence or confidential information from others.
- Cyberterrorism: The use of cyber attacks to create fear, disrupt critical infrastructure, and cause chaos, often with political or ideological motives.
Key components and practices of cybersecurity include:
- Network Security: Implementing measures to protect networks from unauthorized access, attacks, and intrusions. This includes using firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems, and secure network configurations.
- Endpoint Security: Protecting individual devices (endpoints) such as computers, smartphones, and IoT devices. This involves using antivirus software, encryption, and device management solutions.
- Data Encryption: Converting sensitive data into a coded format to prevent unauthorized access. Encryption ensures that even if data is stolen, it remains unreadable without the appropriate decryption key.
- Access Control: Limiting and controlling user access to systems and data based on roles, responsibilities, and the principle of least privilege.
- Authentication and Authorization: Verifying the identity of users and granting them appropriate access permissions based on their roles and responsibilities.
- Security Awareness Training: Educating employees and users about cybersecurity best practices to help prevent social engineering attacks like phishing.
- Incident Response and Recovery: Developing strategies and plans to respond to and recover from cybersecurity incidents, minimizing damage and downtime.
- Vulnerability Management: Identifying and addressing vulnerabilities in software, systems, and networks before they can be exploited by attackers.
- Penetration Testing: Ethical hacking conducted to identify weaknesses in a system’s security, helping organizations proactively address vulnerabilities.
- Security Policies and Procedures: Establishing clear guidelines, protocols, and practices to ensure consistent and effective cybersecurity measures across an organization.
Given the growing reliance on digital systems and the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, cybersecurity has become a critical concern for individuals, businesses, governments, and organizations of all sizes. It’s a constantly evolving field that requires continuous learning and adaptation to stay ahead of emerging threats and vulnerabilities.





