
by admin | Nov 17, 2023 | Digital Marketing, Uncategorized
In the dynamic realm of SEO, where content reigns supreme, guest posting emerges as a potent strategy to not only enhance your website’s visibility but also build valuable relationships within your industry. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the essence of guest posting, why it matters for SEO, and how to execute a strategic guest posting campaign that elevates your online presence.
1. Understanding Guest Posting: A Collaborative SEO Approach
What is Guest Posting?
Guest posting, also known as guest blogging, involves creating and publishing content on someone else’s website or blog. This collaborative approach allows businesses, experts, and content creators to share their insights, knowledge, and expertise with a new audience, gaining exposure and building credibility in the process.
2. The SEO Impact of Guest Posting
2.1 Building High-Quality Backlinks
One of the primary SEO benefits of guest posting lies in the opportunity to acquire high-quality backlinks. When your content is featured on reputable websites within your niche, you not only reach a broader audience but also gain valuable backlinks that signal to search engines the credibility and authority of your site.
2.2 Diversifying Anchor Texts
Strategic guest posting allows you to control the anchor texts used in your backlinks. This diversity in anchor texts contributes to a natural and organic link profile, a factor search engines consider when evaluating the relevance and authority of your website.
2.3 Enhancing Brand Authority
Being featured as a guest contributor on authoritative sites within your industry establishes your brand as an authoritative voice. This increased brand authority not only attracts a more engaged audience but also positively influences your site’s ranking in search engine results.
3. Crafting a Strategic Guest Posting Campaign
3.1 Identify Relevant and High-Authority Websites
Start by identifying websites within your niche that align with your brand and have a strong online presence. Focus on quality over quantity, choosing websites that boast a significant readership and hold authority in your industry.
3.2 Establish Meaningful Relationships
Before reaching out for guest posting opportunities, engage with the target websites. Follow them on social media, comment on their posts, and share their content. Establishing a rapport makes your outreach more personalized and increases the likelihood of a positive response.
3.3 Create High-Quality and Relevant Content
When pitching guest posts, present well-researched, valuable, and relevant topics that align with the host site’s audience. Craft content that not only showcases your expertise but also provides genuine value to the readers.
3.4 Include Authoritative Backlinks
Within your guest posts, strategically incorporate links to your own content, ensuring they enhance the reader’s experience. These links should add value and context rather than merely serving as self-promotion.
3.5 Follow Up and Engage Post-Publication
After your guest post is published, actively engage with the audience through comments and social media. Respond to feedback, answer questions, and continue building relationships within the community.
4. Overcoming Guest Posting Challenges
4.1 Avoiding Duplicate Content Issues
To avoid duplicate content concerns, ensure that the content you submit as a guest post is unique and not replicated from your own website. Customize the content to suit the host site’s audience while maintaining your distinctive voice.
4.2 Selecting Reputable Host Sites
Vet potential host sites carefully. Verify their authority, audience engagement, and overall reputation. Choose websites that align with your brand values and are recognized for providing quality content.
4.3 Balancing Anchor Text Optimization
While it’s crucial to optimize anchor texts for SEO, strive for a natural and diverse mix. Avoid over-optimization, as search engines may view this as manipulative. Aim for a balance that enhances user experience.
5. Measuring Guest Posting Success
5.1 Analyzing Traffic and Engagement
Monitor the traffic and engagement your guest posts generate. Analyze metrics such as page views, time on page, and comments to gauge the impact of your contributions on the host site.
5.2 Tracking Backlink Quality
Use tools like Google Analytics and SEO monitoring tools to track the quality of backlinks generated through guest posting. Evaluate the authority and relevance of sites linking back to your content.
5.3 Assessing Keyword Ranking Improvements
Keep an eye on keyword rankings related to the topics you cover in your guest posts. An improvement in rankings for these keywords indicates the effectiveness of your guest posting strategy.
6. Conclusion: Elevating Your SEO Game with Guest Posting
In the ever-evolving landscape of SEO, guest posting remains a versatile and powerful strategy for enhancing your website’s visibility, building authoritative backlinks, and establishing your brand as an industry leader. By strategically navigating the guest posting landscape, you not only contribute valuable content to diverse audiences but also create a network of meaningful relationships that transcend digital boundaries. As you embark on your guest posting journey, let strategic outreach be the catalyst that propels your brand to new heights of online recognition and influence.
by admin | Nov 17, 2023 | Digital Marketing, Uncategorized
In the complex realm of SEO, where every directive influences search engine behavior, robots.txt emerges as a critical tool for website owners to guide web crawlers and control the indexing of their content. In this guide, we’ll unravel the mysteries of robots.txt, exploring what it is, how it works, and its impact on your website’s search engine performance.
Understanding Robots.txt: The Gatekeeper of Web Crawling
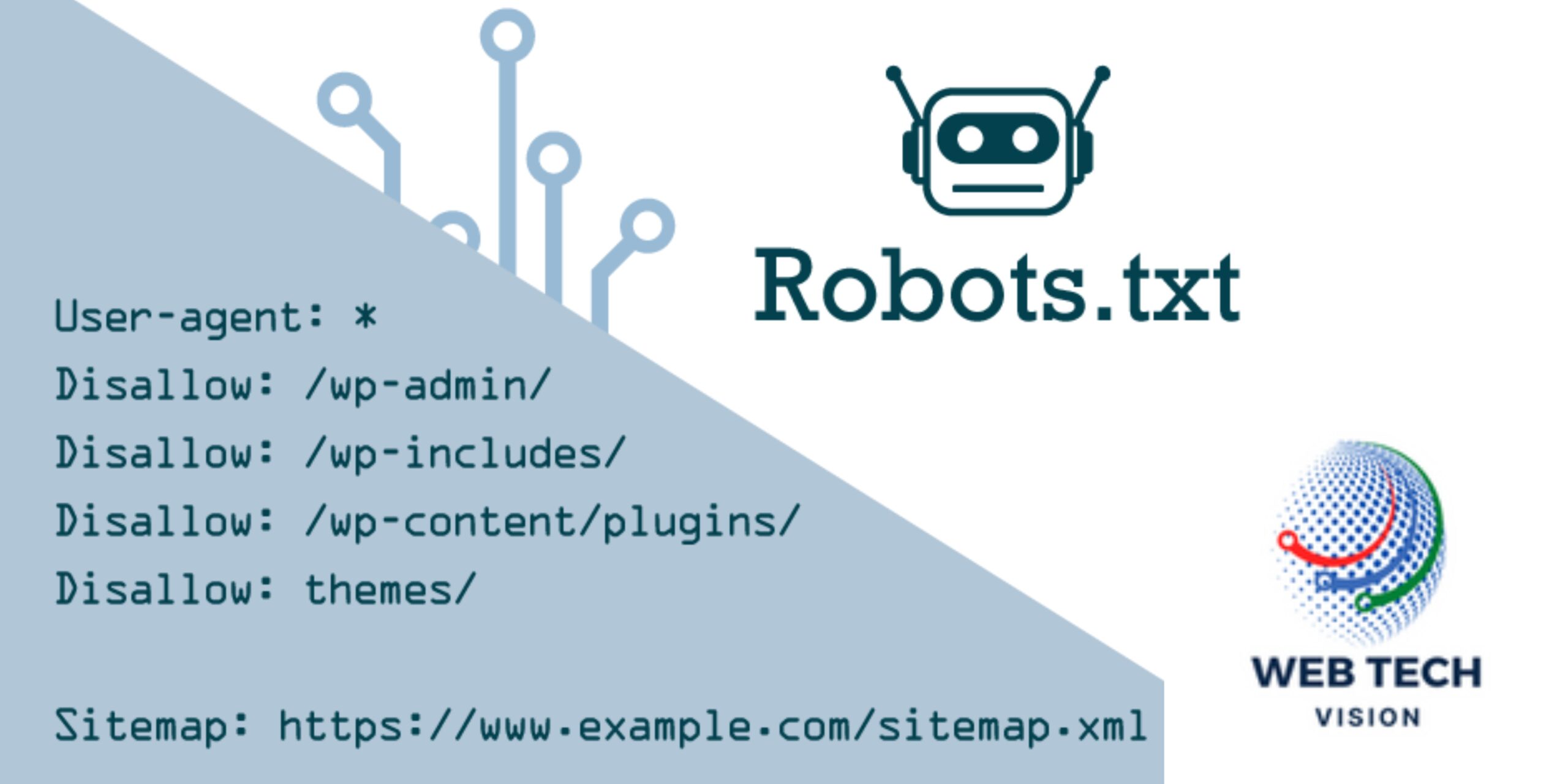
What is Robots.txt?
Robots.txt is a plain text file that website owners create to provide instructions to web crawlers, informing them which parts of the site should be crawled and which parts should be ignored. It serves as a virtual “No Entry” sign for search engine bots, helping to control the flow of information that is indexed.
How Does Robots.txt Work?
When a search engine bot arrives at a website, it first checks for the presence of a robots.txt file in the website’s root directory. If found, the bot reads the directives contained within the file to understand which areas of the site it is allowed to crawl and index.
Key Components of Robots.txt:
- User-agent: Specifies which web crawlers or user agents the directives apply to. For example, Googlebot, Bingbot, or specific bots from other search engines.makefileCopy code
User-agent: Googlebot
- Disallow: Instructs bots not to crawl specific areas of the site. Multiple directives can be used for different sections.javascriptCopy code
Disallow: /private/
- Allow: Permits bots to crawl specific areas even if a broader Disallow directive is present.javascriptCopy code
Allow: /public/
- Sitemap: Informs search engines about the location of the XML sitemap, providing additional guidance for crawling and indexing.arduinoCopy code
Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
Best Practices for Robots.txt:
- Ensure Correct Placement: The robots.txt file should be placed in the root directory of your website to be easily accessible to search engine bots.
- Use Disallow Sparingly: While robots.txt provides control over crawling, excessive use of Disallow directives may unintentionally block important content from being indexed.
- Include Sitemap Information: If available, include a Sitemap directive pointing to your XML sitemap. This assists search engines in understanding the structure of your site.
- Regularly Update: As your site evolves, update the robots.txt file to reflect changes. Regularly check for errors and ensure directives accurately represent your site’s structure.
Conclusion: Navigating SEO Waters with Robots.txt
In the intricate dance between website owners and search engines, robots.txt emerges as a tool for controlled exploration. By carefully crafting directives within this file, you guide web crawlers through the labyrinth of your website, ensuring they prioritize essential content and respect your privacy settings. As you embark on your SEO journey, let robots.txt be the gatekeeper that facilitates a harmonious relationship between your website and the ever-curious search engine bots.

by admin | Nov 17, 2023 | Digital Marketing, Uncategorized
In the intricate world of SEO, where every element of your website plays a role in search engine visibility, XML sitemaps emerge as a critical tool. Let’s unravel the mysteries surrounding XML sitemaps, exploring what they are, why they matter, and how to seamlessly integrate them into your website for enhanced SEO performance.
Understanding XML Sitemaps: The SEO Navigator
An XML sitemap is essentially a roadmap for search engines, providing a comprehensive list of all the pages on your website. Unlike HTML sitemaps designed for human navigation, XML sitemaps are crafted specifically for search engines to crawl and index your content more efficiently.
Why XML Sitemaps Matter in SEO:
- Improved Indexation: By presenting a structured list of your website’s pages, an XML sitemap helps search engines understand the hierarchy and relationships between different sections. This, in turn, facilitates more accurate and comprehensive indexing.
- Faster Discovery of New Content: When you create new pages or update existing ones, the XML sitemap serves as a signal to search engines that there’s fresh content to be crawled. This speeds up the process of discovery, ensuring that the latest information is included in search results.
- Enhanced Crawling Efficiency: For larger websites with intricate structures, XML sitemaps streamline the crawling process. Instead of relying solely on internal links, search engines can use the sitemap to navigate your site more efficiently.
Setting Up Your XML Sitemap: A Step-by-Step Guide
**1. Generate the XML Sitemap: There are various tools available to generate XML sitemaps, including online generators and content management system (CMS) plugins. If you’re using a CMS like WordPress, plugins such as Yoast SEO or Google XML Sitemaps can simplify the process.
**2. Submit to Search Engines: Once you’ve generated your XML sitemap, submit it to major search engines, including Google and Bing. Use Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools to submit your sitemap, allowing search engines to index your pages effectively.
**3. Update and Maintain: Regularly update your XML sitemap to reflect changes in your website’s structure and content. This ensures that search engines always have an accurate representation of your site, promoting efficient crawling and indexing.
SEO Best Practices for XML Sitemaps:
- Include All Relevant Pages: Ensure that your XML sitemap encompasses all significant pages on your website, including blog posts, product pages, and any other content you want to be indexed.
- Prioritize Important Pages: Use priority tags in your XML sitemap to indicate the relative importance of different pages. This guides search engines in prioritizing the indexing of critical content.
- Update Frequency and Last Modified Date: Indicate how often your pages are updated and provide the last modification date. This information helps search engines understand when to revisit and crawl your pages.
- Complement with Robots.txt: While an XML sitemap guides search engines on what to crawl, a well-structured robots.txt file can complement this by indicating what not to crawl.
Conclusion: Navigating SEO Success with XML Sitemaps
In the ever-evolving landscape of SEO, where visibility is synonymous with success, XML sitemaps emerge as indispensable navigational tools. By meticulously crafting and maintaining an XML sitemap, you not only guide search engines through the intricate web of your content but also pave the way for enhanced crawling, indexing, and ultimately, improved search engine rankings. As you embark on your SEO journey, let XML sitemaps be the compass that leads you to the pinnacle of digital success.

by admin | Nov 17, 2023 | Digital Marketing, Uncategorized
“Mastering Keyword Optimization: The Key to SEO Success”
In the intricate world of SEO, where every click matters, mastering keyword optimization is akin to wielding a powerful tool that can elevate your digital presence. Let’s delve into the essence of keyword optimization, exploring its significance, strategies, and the transformative impact it can have on your online visibility.
Why Keyword Optimization Matters:
Keywords are the foundation upon which the edifice of SEO is built. They are the terms and phrases that users type into search engines when seeking information. Strategic keyword optimization ensures that your content aligns with these search queries, increasing the likelihood of your website appearing prominently in search engine results.
Crafting a Strategic Keyword Strategy:
- Thorough Keyword Research: Begin by conducting comprehensive keyword research to identify terms and phrases relevant to your content. Leverage tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to unveil high-impact keywords with significant search volume.
- Understand User Intent: Beyond search volume, understanding user intent is crucial. Tailor your content to match the intent behind the search query, whether it’s informational, transactional, or navigational.
- Long-Tail Keywords: While broad keywords are essential, don’t underestimate the power of long-tail keywords – longer, more specific phrases that often indicate a higher level of user intent and conversion potential.
- Optimize On-Page Elements: Strategically place your chosen keywords in critical on-page elements, including the title tag, meta description, headers (H1, H2, H3), and throughout the body of your content. However, ensure that the integration is seamless and enhances readability.
The Evolving Landscape:
As search engines evolve, so does the approach to keyword optimization. With advancements like semantic search and natural language processing, search engines are becoming more adept at understanding the context and intent behind queries. This shift emphasizes the importance of creating high-quality, relevant content that genuinely addresses user needs.
Avoid Keyword Stuffing:
While keyword optimization is crucial, it’s equally important to avoid keyword stuffing – the excessive and unnatural use of keywords in an attempt to manipulate search rankings. Search engines prioritize user experience, and keyword stuffing can lead to penalties, harming rather than helping your SEO efforts.
Conclusion: Elevating Your SEO Game with Keywords
In the dynamic realm of SEO, where algorithms evolve and user behavior adapts, mastering keyword optimization remains a constant. By strategically aligning your content with user queries and search engine algorithms, you not only enhance your visibility but also provide valuable information that resonates with your audience. As you embark on your SEO journey, let keyword optimization be the compass that guides you to the pinnacle of search engine success.

by admin | Nov 16, 2023 | Digital Marketing, Search Engine Optimisation (SEO)
“Demystifying Heading Tags (H1, H2, H3) for SEO Success: A Comprehensive Guide”
In the realm of SEO (Search Engine Optimization), structuring your content effectively is key to enhancing both user experience and search engine visibility. One crucial aspect of this is utilizing heading tags—H1, H2, and H3. In this guide, we’ll unravel the significance of these tags and how they contribute to SEO success.
H1: The Foundation of Your Content
The H1 tag, or Heading 1, represents the main heading of a page. It holds significant weight in conveying the primary topic or message of your content to both users and search engines. Including relevant keywords in your H1 tag can signal the content’s focus to search engines, potentially improving its ranking.
Example:
htmlCopy code<h1>Unlocking the Power of Heading Tags in SEO</h1>
H2: Subheadings for Structured Content
H2 tags, or Heading 2, function as subheadings under the H1. They help break down the content into sections, making it more readable for users and providing a hierarchical structure for search engines. Including variations of your primary keywords in H2 tags can enhance the overall SEO value of your content.
Example:
htmlCopy code<h2>The Significance of H1 Tags</h2>
H3: Further Subdivision for Clarity
H3 tags, or Heading 3, go a step further in subdividing content under H2 headings. They contribute to a more granular structure, aiding both readers and search engines in understanding the flow of information. Using H3 tags with specific and relevant keywords can refine your SEO strategy.
Example:
htmlCopy code<h3>H1 Tags in SEO: Best Practices</h3>
- Hierarchy Matters: Maintain a logical hierarchy in your heading tags. Follow the sequence of H1, H2, H3 to create a structured and organized content flow.
- Keyword Optimization: Incorporate relevant keywords naturally into your heading tags. This helps search engines understand the context and relevance of your content.
- Consistency is Key: Ensure consistency in your heading tag usage across your website. This uniformity aids both users and search engines in comprehending your content structure.
- Readability for Users: While catering to SEO is essential, remember that heading tags also contribute to a positive user experience. Craft headings that are clear, concise, and enticing for readers.
Conclusion: Elevate Your Content with Heading Tags
In the intricate dance between SEO and user experience, heading tags emerge as crucial partners. By strategically implementing H1, H2, and H3 tags, you not only enhance your content’s visibility on search engines but also provide a more accessible and organized experience for your audience. As you embark on your SEO journey, let heading tags be your allies in conveying the narrative of your content effectively.





